

This involves the equations being solved with simple boundary conditions such as constant surface potential.

These equations can act as simple geometry models for biological systems such as proteins, nucleic acids, and membranes. As expected, the concentration of counter-ions is higher near the surface than in the bulk solution.Ĭ i = c i 0 ⋅ e − W i k B T, A simple planar case with a negatively charged surface can be seen in the figure below. The Gouy–Chapman model explains the capacitance-like qualities of the electric double layer. The entropy of a substance is zero if the absolute temperature is zero. Common thermodynamic terms and functions - potential energy, kinetic energy, thermal or internal energy, chemical energy, nuclear energy and more. For a homogenous isotropic material, the value of shear modulus is.
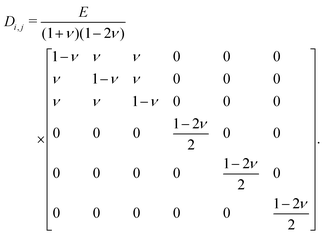
Stern layer is thin compared to particle size fluid velocity = 0 in Stern layer Thermodynamic Terms - Functions and Relations. (Poisson's Ratio) Note: Provide the value in given SI units. Thermal motion of ions accounted for ions behave as point charges įinite ion size ignored uniformly-charged surface non-Coulombic interactions ignored įinite ion size and hydration sphere considered some ions are specifically adsorbed by the surface in the plane, known as the Stern layer Thermal motion, ion diffusion, adsorption onto the surface, solvent/surface interactions considered negligible Surface charge neutralized by a molecular layer of counter-ions surface charge potential linearly dissipated from surface to counter-ions to satisfy charge Poisson ratio is depends on the material. The Stern Layer model goes a step further and takes into account the finite ion size. Poisson’s Ratio Calculator by Mohit Kudal mohitkudal MaAircraft Design / Aircraft Structures / Composite Materials / Engineering Calculator Poisson’s ratio is the relation between lateral strain and longitudinal strain. Due to thermal motion of ions, the layer of counter-ions is a diffuse layer and is more extended than a single molecular layer, as previously proposed by Hermann Helmholtz in the Helmholtz model. In the Gouy-Chapman model, a charged solid comes into contact with an ionic solution, creating a layer of surface charges and counter-ions or double layer. The Poisson–Boltzmann equation describes a model proposed independently by Louis Georges Gouy and David Leonard Chapman in 19, respectively. where the gravitational potential satisfies the Poisson equation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
